| The Very Highest Quality Gemstone Information... |
| Dispersion |
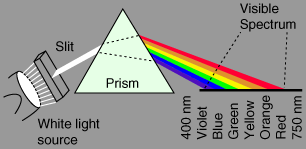 Dispersion of Light |
Definitions
The divergence or spreading of the different coloured rays of a beam of composite light when refracted by a prism or lens, or when diffracted, so as to produce a spectrum, especially in reference to the amount of this dispersion. (O.E.D.)
The power of a transparent medium to separate the spectrum colours.the figures being usually the result of the subtraction of the figures of refractive index for the red ray ("B" line at 6867Ä.) from the figures of the refractive index for the violet ray ("G" line at 4308Ä.). (Gemmologist's Compendium by Webster)
Dispersion
Dispersion is the difference between the amount of refraction of different colours of light. White light is actually composed of light of all different colours. A highly dispersive material will split light strongly into its component colours to give a "prism" effect showing a "rainbow" or spectrum.
Dispersion is often known as "fire".
Diamond owes most of its beauty to its high dispersion, whereas white sapphire, with low dispersion tends to look "dead" or glassy.
Dispersion of Various Gems and Minerals
| Name | Dispersion |
| Fluor | 0.007 |
| Calcite (e-ray) | 0.008 |
| Calcite (o-ray) | 0.017 |
| Silicon Glass | 0.010 |
| Beryllonite | 0.010 |
| Leucite | 0.010 |
| Cancrinite | 0.010 |
| Kyanite | 0.011 |
| Pollucite | 0.012 |
| Feldspar | 0.012 |
| Apatite | 0.013 |
| Brazilianite | 0.014 |
| Beryl | 0.014 |
| Topaz | 0.014 |
| Smithsonite (o-ray) | 0.014 |
| Smithsonite (e-ray) | 0.031 |
| Hambergite | 0.015 |
| Phenakite | 0.015 |
| Chrysoberyl | 0.015 |
| Fibrolite | 0.015 |
| Euclase | 0.016 |
| Danburite | 0.016 |
| Datalite | 0.016 |
| Crown Glass | 0.016 |
| Andalusite | 0.016 |
| Iolite | 0.017 |
| Tourmaline | 0.017 |
| Spodumene | 0.017 |
| Scapolite | 0.017 |
| Corundum | 0.018 |
| Kornerupine | 0.018 |
| Sinhalite | 0.018 |
| Idocrase | 0.019 |
| Peridot | 0.020 |
| Spinel | 0.020 |
| Kyanite | 0.020 |
| Pyrope Garnet | 0.022 |
| Staurolite | 0.023 |
| Almandine Garnet | 0.027 |
| Hessonite Garnet | 0.027 |
| Spessartite Garnet | 0.027 |
| Willemite | 0.027 |
| Dioptase (o-ray) | 0.028 |
| Dioptase (e-ray) | 0.036 |
| Epidote | 0.030 |
| Zircon | 0.038 |
| Flint Glass | 0.041 |
| Diamond | 0.044 |
| Anglesite | 0.044 |
| Benitoite | 0.044 |
| Sphene | 0.051 |
| Demantoid Garnet | 0.057 |
| CZ, C.Z., Cubic Zirconia | 0.06 |
| Cassiterite | 0.071 |
| Moissanite | 0.104 |
| Blende | 0.156 |
| Strontium Titanate | 0.19 |
| Anatase (o-ray) | 0.213 |
| Anatase (e-ray) | 0.259 |
| Rutile | 0.28 |
Notes
O-Ray = Ordinary ray
E-Ray = Extraordinary ray, a ray in doubly refractive uniaxial mineral in which the velocity varies according to the direction in which it passes through the crystal.
You may wish to visit some of our other pages:-
Gemstone Characteristics
Hardness - Moh's Scale
Refractive Index
Specific Gravity or Density
A to Z of Gemstones
| ...at the Lowest Possible Price |
|
32 - 36 Harrowside, Blackpool, Lancashire, FY4 1RJ, England. Telephone (44) - (0) 1253 - 343081 ; Fax 408058; E-mail: The URL for our main page is: https://24carat.co.uk | Chard(1964) Ltd |